Introduction
The Advanced Energy Catalysis and Porous Functional Materials group is affiliated to
Zhengzhou Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Catalytic Materials Preparation Technolog,
headed by Prof. Jianan Zhang. Our group is mainly engaged in basic research of energy
conversion materials and energy storage materials, mainly including
Multi-scale carbon composite design and the study of confined effect, focusing on the development of new efficient carbon-ba
sed non-noble metal electrocatalysts.
Relying on the non-noble metal or transition metal carbon-based catalyst efficient catalytic reaction, for example, ORR, OER,
HER, CO2RR, NRR and NITRR
Key scientific and technological issues in the development of energy storage devices like metal ion battery and lithium sulfur battery.
The simulation calculation and theoretical modeling of catalytic process provide basic scientific basis for the optimization and development of catalyst and explain the source of catalytic activity and reaction mechanism.
Structure-activity Design of Carbon-based Catalysis
Electrocatalysis plays an important role in energy storage and conversion technologies, such as metal air cell, fuel cell, water electrolysis and so on, and the development of efficient electrocatalyst is one of the core research contents. Carbon-based materials have an important application prospect in the field of energy electrocatalysis because of their advantages of adjustable structure, easy doping, good conductivity and low cost. The group focuses on the preparation of carbon-based monatomic catalysts, carbon-based hetero-atom doped catalysts, carbon-based coated catalysts and carbon-based supported catalysts using non-precious metals. It aims to achieve high efficiency, high selectivity and low-cost catalysis.
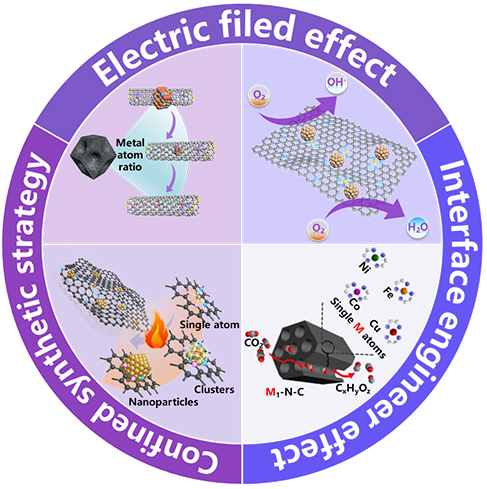
Energy Molecules Conversion & Catalysis
Electrocatalysis plays an important role in energy storage and conversion technologies, such as metal air cell, fuel cell, water electrolysis and so on, and the development of efficient electrocatalyst is one of the core research contents. Carbon-based materials have an important application prospect in the field of energy electrocatalysis because of their advantages of adjustable structure, easy doping, good conductivity and low cost. The group focuses on the preparation of carbon-based monatomic catalysts, carbon-based hetero-atom doped catalysts, carbon-based coated catalysts and carbon-based supported catalysts using non-precious metals. It aims to achieve high efficiency, high selectivity and low-cost catalysis.
Computational and Theoretical Modeling of Energy Catalysis Processes
Rational design and optimization of catalyst toward high reactivity and selectivity requires clear understanding of the activation mechanism, reaction mechanism, and the underlying factors that determine the reaction thermodynamics and micro-kinetics at an atomic level. This is rather challenging due to the complexity in catalyst structure and composition and the reaction network, and the limited information that is obtained from experimental characterizations. Here, we employ theoretical and computational che
mistry tools to simulate catalytic conversion of energy molecules and obtain the key information about the reaction systems, i.e.
the active centers, reaction mechanisms, and structure-reactivity relationships, etc., aiming to provide insights into the nature of carbon-based materials in catalytic conversion of energy molecules for rational design and screening of carbon-based material
catalysts.
have an important application prospect in the field of energy electrocatalysis because of their advantages of adjustable structure, easy doping, good conductivity and low cost. The group focuses on the preparation of carbon-based monatomic catalysts, carbon-based hetero-atom doped catalysts, carbon-based coated catalysts and carbon-based supported catalysts using non-precious metals. It aims to achieve high efficiency, high selectivity and low-cost catalysis.
have an important application prospect in the field of energy electrocatalysis because of their advantages of adjustable structure, easy doping, good conductivity and low cost. The group focuses on the preparation of carbon-based monatomic catalysts, carbon-based hetero-atom doped catalysts, carbon-based coated catalysts and carbon-based supported catalysts using non-precious metals. It aims to achieve high efficiency, high selectivity and low-cost catalysis.
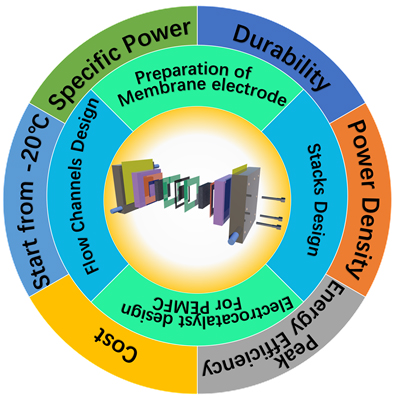
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
The large-scale application of proton exchange membrane fuel cells(PEMFC) is severely hampered by the slow kinetics of the cathodic oxygen reduction reaction. Our group has achieved excellent results in improving the activity of low-Pt/Pt-free metal catalysts by means of Confinement Strategy, defect engineering, and spin state modulation. At this stage, we have started to focus on the degradation problems of fuel cell catalysts to ensure high catalyst activity while meeting the fuel cell lifetime requirements.
We used membrane electrodes prepared by hot pressing method to test the power density and durability of fuel cells, which was tested at 80°C with hydrogen as the anode and oxygen as the cathode.
(Adv. Sci. 2022, 2200147; Adv. Function. Mater. 2022, 2113191; Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 1734; Adv. Sci., 2021, 2102915; ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 12754-12762)
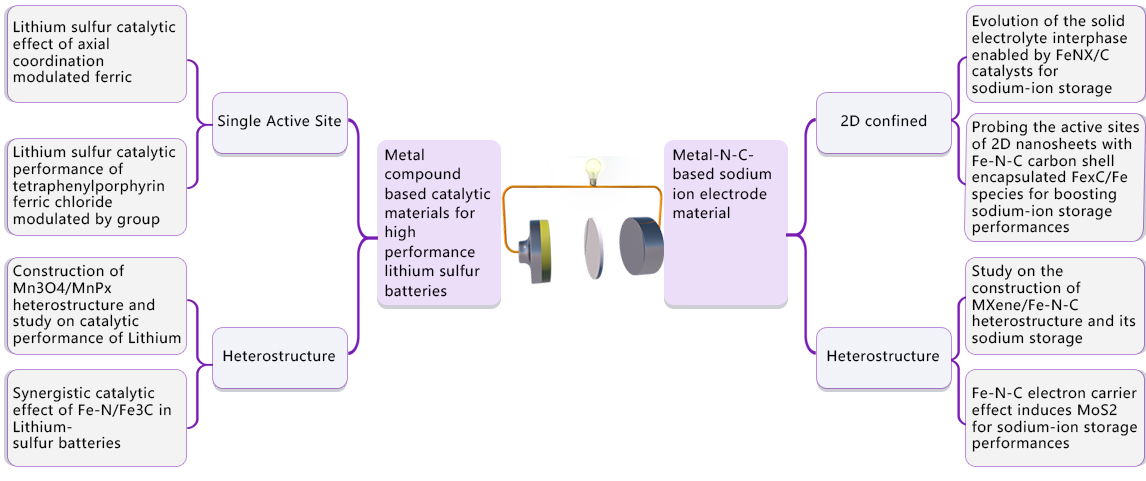
Electrode Materials of Sodium-ion Batteries & Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
The structure and chemical engineering of a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) play a vital role in metal-ion batteries. The underly
ing correlation between the properties of the enhanced sodium/lithium-ion storage and SEI in metal–nitrogen platform electrodes was not revealed during charging and discharging cycles. Here, we focus on exploring metal–nitrogen-based anode materials for metal-ion batteries, aiming to obtain a qualitative understanding of the properties of metal–nitrogen-based materials that determi
ne the capacity of a metal-ion battery, and to develop a potential anode material for the efficient use of an SEI.
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries are a new generation of energy storage devices due to their high specific capacity and high energy density. We are exploring efficient catalysts to accelerate the reaction rate of LiPSs→Li2S1/2 conversion, improving the electrochemical performance of Li-S batteries. We focus on the modulation of single-site catalysts (SSCs), such as metal-phthalocyanine, metal-porphyrin, and metallocene, etc. Furthermore, we are aiming at correlating the spin state of the active metal center with the catalytic effect in Li-S batteries. The exploration of SSCs provide new routes for the design of catalysts in Li-S batteries.
(Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 46, 322-328; Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15, 771-779 ; Energy Storage Mater., 2021,36,496-503; Na
no Res. 2021, DOI:10.1007/s12274-021-3992-9; J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 15358-15372; J. Collid. Interf. Sci., 2019, 557, 635–643)